ESM-Tests
Note
This is a feature aimed for advance users and developers who work in preparing default configurations of experiments, or who implement a model/coupled-setup in ESM-Tools.
ESM-Tests is the integration testing suite from ESM-Tools. Its aim is to test a set
of selected runscripts and model builds just by using one single command:
esm_tests. It can also perform dry actions (i.e. check compilations and check
runs).
Glossary
- actual vs check test
An actual test is a test where the model has been compiled and run in one of the supported HPCs. A check test is a dry test, meaning, no compilation or run takes place, but instead, the configuration files and scripts are generated. Both actual and check tests compare their output configuration files and scripts to the last-state, and offer the possibility to update the last-state of those files at the end of the test.
- esm_tests_info
The repository where the files of the
last-stateand therunscriptsfor testing are stored. This repository is clone as a submodel of ESM-Tools wheneveresm_testscommand is run for the first time. The repository is cloned locally into theesm_tools/src/esm_tests/resourcesfolder. You can activate the submodule manually viagit submodule initfollowed bygit submodule sync.- last-state
Set of configuration files, both from compilation and runtime, that represent the last approved configuration of the testing runscripts. This set of files is kept for comparison with the equivalent files of future pull-requests, to ensure the stability of the configurations. ESM-Tests always compares the new files to the
last-statefiles automatically, both in actual compilation/runs or check compilation/runs. See Last-state.- runscripts
The runscripts to run the tests. Runscripts define the test simulation details as in regular ESM-Tools runscripts, but are also used for ESM-Tests to understand what needs to be compiled. Runscripts are part of the
esm_tests_infosubmodule, and can be found (if the submodule was initiated viaesm_tests -u) inesm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts. Runscripts need to be generalized (i.e.choose_computer.name) for the different HPCs where you want to run the tests.state.yamlIn this document some times referred only as state, is a YAML file that includes information about the status of the tests (actual tests or check tests) in different computers. It also includes the date of the last actual test.
Usage
ESM-Tests is designed to compile and run tests just with one single command,
without additional arguments: esm_tests, so that launching a suite of tests in a
supported HPC is straight forward. Higher granularity in the control of the tests is
enabled via:
Runscripts via the usual
esm_parsersyntax (e.g.choose_computer.name)
The commands syntax is as follows:
esm_tests [-h] [-n] [-c] [-u] [-d] [-s SAVE] [-t] [-o] [-b] [-g] [-e] [-r BRANCH]
Arguments
Optional arguments |
Description |
|---|---|
-h, –help |
Show this help message and exit |
-n, –no-user |
Avoid loading user config (for check tests in GitHub) |
-c, –check |
Check mode on (does not compile or run, but produces
some files that can be compared to previous existing
files in |
-u, –update |
Updates the resources with the release branch, including runscriptsand last_tested files |
-d, –delete |
Delete previous tests |
-s SAVE, –save SAVE |
Save files for comparisson in |
-t, –state |
Print the state stored in |
-o, –hold |
Hold before operation, to give time to check the output |
-b, –bulletpoints |
Bullet points for printing the state and copy/paste as markdown text |
-g, –github |
Use this flag when running in GitHub servers (i.e. adds syntax for collapsing compare sections of the output for GitHub Actions) |
-e, –system-exit-on-errors |
Trigger a system exit on errors or file differences so that GitHub actions can catch that as a failing test |
-r BRANCH, –branch BRANCH |
use the given esm_tests_info branch |
Last-state
The last-state files are https://github.com/esm-tools/esm_tets_info repository, in
the release branch. The files stored in the last-state are:
* compilation scripts (comp-*.sh)
* namelists
* namcouple
* finished_config
* batch scripts (.run)
Check test status
As a user, you can check the last-state status (the online one of the
esm_tests_info repo, release branch) by running:
esm_tools test-state
This will give you a summary of the state of compilation and running tests for different models, in different computers, and also a date of when the latest actual compilation and run tests were carried out.
If you are testing locally in an HPC, you can get the same information about your local state by running:
esm_tests -t
Model control file (config.yaml)
File location: esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/config.yaml
Versioned: Yes, distributed with esm_tests_info
The Model control file gives you control over ESM-Tests setups for the set of
runscripts for a given model (the model which name is the same as the folder where
the config.yaml is contained:
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/).
Within this file you can control:
which files need to be present for considering an
actual compilation testsuccessful (comp.actual.files)which files need to be present for considering an
actual run testsuccessful (run.actual.files)which messages from the execution of
esm_runscriptsshould trigger an error in anactual run test(run.actual.errors)which
computersare supported for this set of tests (computers)
The file should contain this structure:
comp:
actual:
files:
- "file/path" # Typically the binaries
check: {}
run:
actual:
errors:
- "error message to mark the test as not successful # Typically "MISSING FILES"
files: # Typically restart files and outdata files
- "path/to/file1"
- "globbing/path/*/to*files"
check: {}
computers:
- <computer1>
- <cimputer2>
In the files sections, globbing is supported.
The file’s paths should be relative to the compilation folder or the experiment folder.
Each file name can be followed by the syntax in/except [<model_version1>,
<model_version2>, ...] to only check for that file in that set of model versions,
or to exclude (except) that file from being check for a set of model versions.
Example
comp:
actual:
files:
- "bin/fesom*"
- "bin/oifs"
- "bin/rnfma"
check: {}
run:
actual:
errors:
- "MISSING FILES"
files:
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/hnode.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/salt.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/ssh_rhs_old.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/temp.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/urhs_AB.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/vrhs_AB.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.oce.restart/w_impl.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/area.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/hice.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/hsnow.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/ice_albedo.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/ice_temp.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/uice.nc*"
- "restart/fesom/fesom.*.ice.restart/vice.nc*"
- "restart/oasis3mct/rmp_*"
- "restart/oasis3mct/rstas.nc*"
- "restart/oasis3mct/rstos.nc*"
- "restart/oifs/*/BLS*"
- "restart/oifs/*/LAW*"
- "restart/oifs/*/rcf"
- "restart/oifs/*/srf*"
- "restart/oifs/*/waminfo*"
- "outdata/oifs/*/ICMGG* except [frontiers-xios, v3.1]"
- "outdata/oifs/*/ICMSH* except [frontiers-xios, v3.1]"
- "outdata/oifs/*/ICMUA* except [frontiers-xios, v3.1]"
- "outdata/oifs/atm_remapped* in [frontiers-xios, v3.1]"
- "outdata/fesom/*.fesom.*.nc"
check: {}
computers:
- ollie
- mistral
- juwels
- aleph
- blogin
- levante
Local test configuration (test_config.yaml)
File location: esm_tools/src/esm_tests/test_config.yaml
Versioned: No, user specific, git-ignored
This file gives you control on which tests esm_tests will run in the current
machine, independently of what tests are defined in the Model control files. The
current machine needs to be included in the Model control file for the test to run
(i.e. test_config.yaml runs only the tests included there and supported on the
current platform). The syntax is as follows:
<model1>: - <runscript1_name>.yaml - <runscript2_name>.yaml - [ ... ] <model2>: all [ ... ]
The model sections need to be named after the folders in
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts. If you want to run all the suported
runscripts for a model in this platform, make the model section have the value
all. If you want to select a set of supported runscripts make the model
be a list of runscripts (this runscripts need to be in
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/). If you want to run all the
supported runscripts for all supported models in this platform, but still keep this
file around (i.e. commented most of the contents), make the file content be an empty
dictionary ({}).
Example
#{} awiesm: #all - all_awiesm-2.1-recom.yaml # - awiesm-2.1_icebergs.yaml - bootstrap.yaml - pico.yaml - PI_ctrl_awiesm-2.1-wiso.yaml - pi.yaml - pi-wiso.yaml echam: all fesom: all awicm: all # - awicm1-CMIP6-initial-monthly.yaml # - awicm2-initial-monthly.yaml fesom-recom: - fesom-recom1.4-initial-daily.yaml awicm3: all # - awicm3-v3.1-TCO95L91-CORE2_initial # - awicm3-frontiers-TCO159L91-CORE2_initial.yaml #oifsamip: all #vilma-pism: all
ESM-Tests cookbook
How to include a new model/runscript
Add the given runscript to
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/Make sure your runscript has a meaningful name
Make sure your runscript has the correct model
versiondefined, for a standalone model in the section of the model (not ingeneral), and for a coupled setup, both in thegeneralsection and in the coupled setup section (e.g.awiesmsection). This version will be used by ESM-Test for theesm_mastercommand to compileModify the following variables to take the environment variables setup by ESM-Tests:
general: account: !ENV ${ACCOUNT} base_dir: !ENV ${ESM_TESTING_DIR} <standalone-model/setup>: model_dir: !ENV ${MODEL_DIR}
Generalize the runscript to be able to run in the computers where you’d want it to be supported (i.e. add the necessary
choose_computer.nameswitches)Create the Model control file (
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/config.yaml). See ref:esm_tests:Model control file (``config.yaml``) for details about the contentIf you are using the Local test configuration (``test_config.yaml``) to exclude some models, make sure the current model is included, so that your tests can be run locally.
How to include a new platform for in an existing model
In the corresponding Model control file (
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/config.yaml), add the name of the platform to thecomputerslistIn the runscripts (
esm_tools/src/esm_tests/resources/runscripts/<model>/<runscript>.yaml), add the necessary case to thechoose_computer.nameto specify pool directories, forcing files,nproc, etc.
How to approve changes on a GitHub Pull-Request
In the pull-request, if all the tests passed you don’t need to approve any changes, you can jump directly to step 4.
If any of the tests labelled as
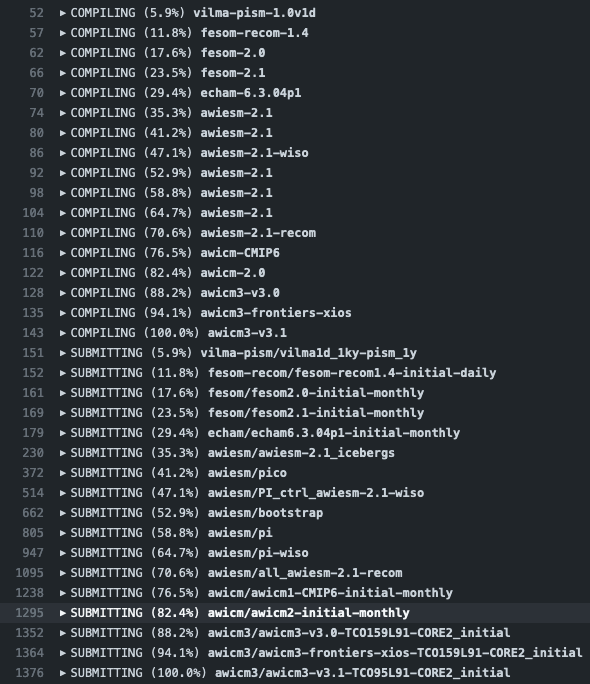
esm_testsfailed (click on the triangles to expand screen captures):Click on Details
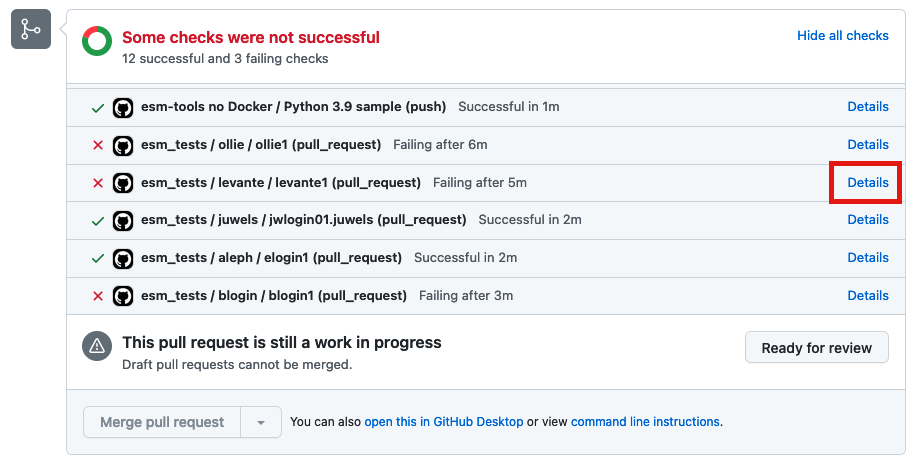
Find the names of the runscripts with differences (in yellow)
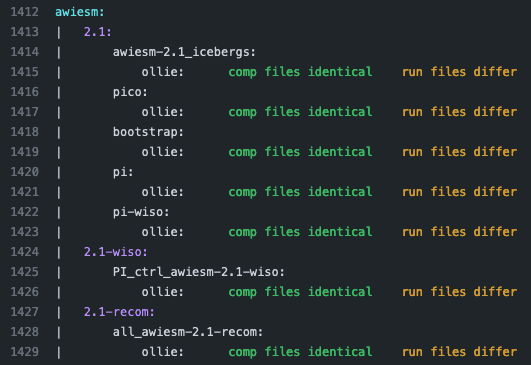
Review the differences with special attention to namelists and namcouple files
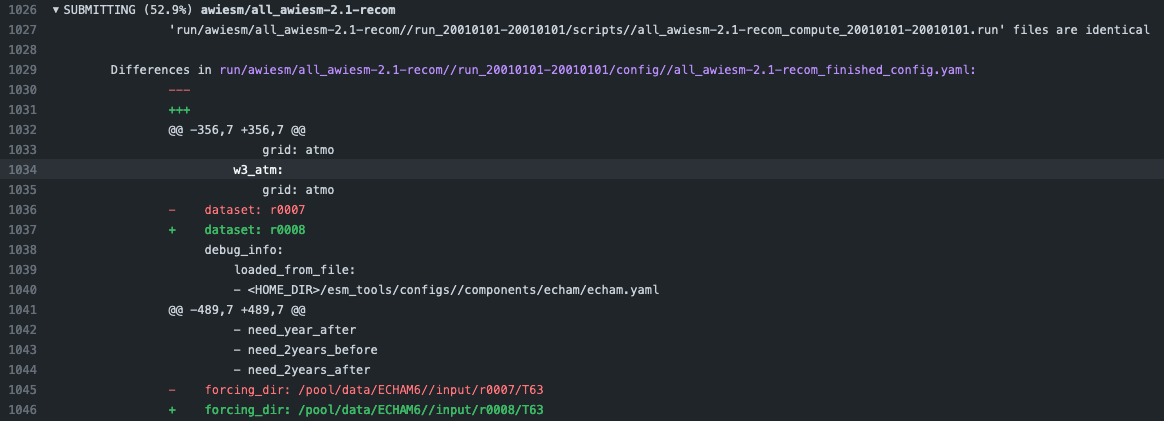
If there are no problematic differences, and the pull-request has been already reviewed and is just ready to be merged, write a message on the PR containing
#approve-changes. This will commit the new files from the tests as thelast-state, in theesm_tests_inforepository.Warning
Currently,
#approve-changesdoes not update the test status on GitHub, once the operation finishes. If you want to see whether#approve_changesfinished or not you have to navigate to theActionstab in GitHub. If you want to see all tests green, wait until#approve-changesfinishes, and relaunch the tests for the last failed set of tests in the PR. Miguel - I know this is a pain, but I could not figure out how to do all this automatically (I wasted enough time on GitHub Actions for years to come).Bump the version and wait that the bumpversion commit shows up.
You can now merge.